Panel discussion on...
Healthy lifestyle
Welcome in the world of alternative meat: analytical challenges and perspectives

Introduction
1) One trend that has been noticeable is a move from health at all costs, to considered health, with consumers placing less priority on spending within the health and wellness market. Consumers are still spending but are scrutinizing more closely whether products are good value for money, effective, and essential. In addition, there has also been a move away from a focus on fear of illness, to addressing day-to-day well-being issues, such as mood and energy levels.
2) One interesting area has been the advances in protein hybrids, which serve both a functional, nutritional, and sustainable purpose. Indeed, the hybrid mixtures and opportunities around fortification not only address concerns over sensory appeal, but also the worry that plant-based diets are lacking certain nutrients. Moreover, while this section of the plant-based market will witness some backlash, it does appear a logical step to help facilitate meat reduction at a time when food supply chains become increasingly inadequate.
3) The main area of research that we have seen has been within the gut microbiome and establishing the link between the digestive system and other areas of well-being, including emotional health. While this has been a key area of innovation, and creates opportunities around personalization and customization, I do think long-term, more needs to be done to be descriptive and educative about what brands mean by “gut” and “digestive health”.
4) Price is the obvious answer to this, but it must be remembered that value is more important than low cost, and that value is ultimately determined by perceptions of efficacy. This means that consumers want products with multifunctional benefits (especially if they are taking a proactive approach to health and not suffering specific symptoms), and they want these benefit claims to be validated via scientific claims and evidence.
5) How do consumer today judge their health status: Please put the following parameter in order.
Emotional wellness is a major issue in an era of uncertainty and consumers evaluate their emotional wellness based on how they feel and what they see in the mirror. This is how we would rank priorities from 1 (highest) to 7 (lowest):
1. Mental and emotional well-being.
2. Diet and nutrition.
3. Quality of sleep.
4. Fitness levels.
5. Physical symptoms.
6. Medical check-ups.
7. Health tracking devices.
6a) While capsules and tablets remain the most popular form of supplement, there has been a surge in the popularity of formats that blur the boundaries of food and supplement, such as jellies and gummies.
6b)The desire for gummies and jellies appears, at least from a consumer perspective, to be especially noticeable in North America and Asia-Pacific over Europe.
7) Across the globe, there has been a significant increase in the proportion of consumers placing greater emphasis on mental well-being and sleep health over the last couple of years, which can be linked to people facing various levels of uncertainty that impact emotional wellness.
Concern over emotional wellness is more noticeable in North America and South America compared to Asia-Pacific and Europe. In comparison, consumers in Asia-Pacific are more noticeable than the global average to want to improve digestive health.
8a) At the moment, I would say consumers still have a preference for supplements over apps, even if the apps are more personalized. The reason for this is that consumers can find it difficult to monitor apps and may lack certainty over effectiveness, whilst supplements are positioned around ingredients that are known and trusted and involve less daily routine.
8b) One trend that has become more noticeable in recent years is that consumers can sometimes feel that health and wellness brands are too generic and not suited to their specific needs. The ability to monitor health and nutrient in-take in real time via apps is something that has definitely helped shape these attitudes.
10) The ethical and environmental credentials of a brand are important to consumers, especially as they deem health and sustainability to be interlinked, meaning they want brands to demonstrate accountability along the supply chain. Linked to this, consumers also want to avoid ingredients that sound artificial and potentially damaging to the environment. However, while sustainability claims are important to consumers, it is important not to overestimate the influence of these claims on purchasing alone, or willingness to pay a premium.
Consumers can demonstrate an attitude/behavior gap when it comes to sustainability claims. Indeed, consumers state that they deem these claims to be important, but this is only a secondary consideration when purchasing products compared to other attributes such as taste, nutritional profile, convenient format, and price.
What is required to scale-up production of alternative protein sources, such as lab-grown meat and cultivated (breast/bovine) milk?
For the production of 1 kg meat approx. 1 thousand times more water is needed than for 1 kg grain. And furthermore 60% of grain production in Germany is used for feeding cattle and pork.
The development of automated production equipment for tailor-made cultured meat using 3D bioprinting will help to feed the world (4).
The 3D bioprinting technology was developed by Professor Matsusaki of the Osaka University to create muscle tissue structures. This technology is expected to be utilized in the field of food, for production of cultured meat with controlled arrangement of muscle, fat, and blood vessels.
Most of the cultured meats reported so far have a minced structure consisting only of muscle cells, making it difficult to reproduce complex structures. To solve this problem, Matsusaki and co-workers developed a 3D bioprinting technology that uses 3D printing to produce different fibrous tissues (muscle, fat, and blood vessels) and integrates them into a bundle. This technology has made it possible not only to reproduce the famous Wagyu beef, but also to delicately adjust the fat and muscle components. Osaka University and Shimadzu will jointly develop equipment to automate the production of cultured meat using this technology. (5).
What are the most effective methods for enhancing the flavor and texture of alternative proteins?There are meaningful reasons not to go for these new types of foods
Bad experience in terms of taste and texture
Raw meat on its own has little aroma; therefore, almost all aromas associated with “meatiness” are created during the cooking process by the Maillard Reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars. That reaction determines which non-volatile precursors release volatile aroma compounds. Plant-based meat (PBM), products created to resemble animal meat in both look and taste, are growing in popularity. A plant protein such as soy protein concentrate, along with colors, stabilizers, and oils, is used to successfully mimic meat flavor and texture. And, just like in animal meat, the amino acids of that protein undergo the Maillard Reaction.
Samples of PBM were run with the solid phase microextraction GC-MS and the volatile profile was compared against that of the organic beef. Similar compounds, such as fatty acids and Maillard browning reaction products, were found in both types of meat (Figure 1).
The differences can be explained by the different and wide variety of precursors present in PBM since it contains amino acids and sugars from various sources as opposed to regular meat.
There are five basic tastes, including deliciousness, which are perceived by people. The amount and kind of amino acids contribute to taste components. Of all the amino acids, glutamic acid is widely known as a component of the delicious taste. Further, the types and component ratios of amino acids largely control the flavor of food products. For example, glycine and alanine are associated with sweetness, valine and leucine with bitterness, and aspartic acid and glutamic acid with deliciousness.
The texture of food, including the sense of crispness, springiness, firmness, and the feeling on the tongue, is an important element that together with taste has an impact on the deliciousness of food. Food texture is normally evaluated using sensory tests. However, sensory tests are often difficult to reproduce, due to individual differences in people’s sensations and physical condition.
A texture analyzer can support sensory test with objective results in the form of numerical values for use in the field of food development. The texture analyzer evaluates the texture characteristics and allows a comparison of the texture of plant-based meat (PBM) and, for instance, chicken meatballs. Compared to chicken-derived products, plant-based meatballs had a higher force under loading conditions with less elasticity, which is the property to restore deformation (6). It is consistent with the result of the sensory test.
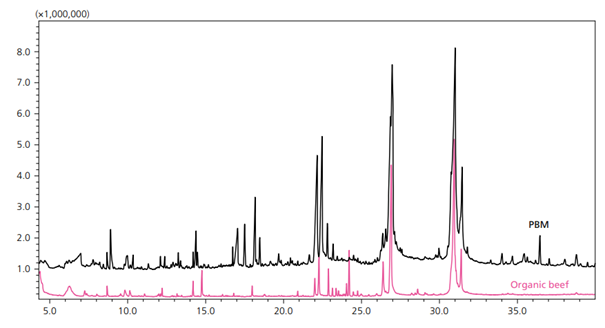
Figure 1. Overlaid Representative Chromatograms for PBM (black) and Organic Beef (pink) (6).
Panelists
References and notes
- Kaplan, A. 2021. Artificial Intelligence (AI): When Humans and Machines Might Have to Coexist. In: Verdegem, P. (ed.) AI for Everyone? Critical Perspectives. Pp. 21–32. London: University of Westminster Press. DOI: https://doi.org/10.16997/book55.b. License: CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0
Questions
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
How have consumer awareness & demands related to healthy lifestyle changed in the last 12 months?
Where do you see the greatest scientific achievement in nutritional sciences in the last 12 months?
Are there specific health benefit areas in which significant more clinical studies are being done than in others, comparing the last 3 years?
What are the key influencers driving consumer purchasing decision for supplements or health foods? Is substantiation of claims important?
How do consumer today judge their health status?
Please put the following parameter in order 1 highest priority 7 lowest priority:
- Physical Symptoms, like pain, fatigue, constipation, weight gain
- Fitness Levels: endurance, strength, flexibility,
- Health Tracking Devices and heart rate, sleep patterns, steps taken
- Diet and Nutrition: intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins.
- Mental and Emotional Well-being: stress levels, emotional balance, happiness
- Quality of sleep: Sleep quality and duration
- Medical Check-ups: blood pressure checks, cholesterol screenings, blood sugar tests
6.
Delivery formats can support consumer compliance and underline the technology driven approach of the brand.
a.
b.
c.
Do you see a consumer trend in preferences for certain delivery formats?
Are delivery format preference a regional, cultural aspect like taste?
Do you see a trend to carry out ingredient clinical trials using a selected delivery format as study product formulation or are most clinical studies still done in capsules?
7.
Consumer health concerns can vary widely across different regions and demographics globally. However, several common health concerns tend to be prevalent across various countries and populations due to globalization, lifestyle changes, environmental factors, and access to information.
a.
b.
Which are the key global consumer health concerns?
Do you see regional differences?
8.
There is a significant increase in the availability of apps and digital platforms focused on healthy lifestyle, particularly to support personalized approaches to mental wellbeing, metabolic support, weight management and physical fitness.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Do you see lifestyle apps as competition for supplement brands?
Do you think that these apps help to educate consumers, being more targeted when searching for supplements?
Did you consider setting up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement or your ingredient?
Did you set up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement/ ingredient and can you explore about your experience and business impact?
9.
AI (Artificial Intelligence) algorithms are today offered for various aspects of clinical trials to proof efficacy of your health ingredient or supplement.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Are consumers looking for substantiation of claims through AI driven clinical trials?
Did you consider working with an CRO specialist in AI to investigate your health ingredient or supplement?
If you applied already AI methods during the discovers/ development of your health ingredient, please share your experience and recommendation with us.
Do you think that in 2030 AI will be a manifest tool for clinical trials?
10.
A healthy lifestyle may also involve a commitment to sustainable practices for both personal and planetary health. This could include supporting ethical and environmentally conscious products.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Do you agree that sustainability has become a growing concern also in the nutraceutical industry?
Are consumer looking proactively for brands which have ethical and environmental principles?
Are you looking for ethically sourced raw materials, ingredients?
Did you implement measures to establish resource-efficient processes?
Are you developing socially useful products and how do you define it?
11.
What are the major geographical differences related to healthy lifestyle trends?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
What are the latest trends related to claims and product forms in China?
In the U.S.
In Mexico
How are claims and dosage forms differentiated in Europe? How does your company ensure compliance with health and safety regulations in Europe?
Do you have a country where you would like to speak about trends for products?
12.
Focus clinical studies. Overall, there has been a recognized push for more gender-inclusive, geographical, and target group focused clinical research. The same trend can be seen in clinical trials for supplements or functional foods.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Please select an area you are active in and let us know which is your hot topic ingredients for 2024 for this area, based on substantiated claim, parameters, biomarkers being studied and/ or clinical study being done. Please name ingredients by scientific name and composition and not by brand name.
Please select your geographical area:
Western (EU, USA)
Asia (China, Japan, Asia Pacific)
Americas (Middle and Latin America)
Kids development/ early life nutrition/infant in Western countries and AP
Adult nutrition and prevention of developing disease
Elderly nutrition and how to support quality of life during aging
Sports nutrition, within different life decades and activity levels
References and notes























