Panel discussion on...
Healthy lifestyle
Welcome in the world of alternative meat: analytical challenges and perspectives

Introduction
1) More than ever, since the COVID-19 pandemic, prevention has become a hot topic among consumers. They are more informed about the importance of healthy lifestyles in avoiding possible future illnesses and conditions. They are well aware of the close links between nutrition and health, and the impact that good nutritional habits can have on their general well-being.
On the other hand, the definition of wellbeing has also evolved, moving from a purely physical-based definition to a holistic concept encompassing mental wellbeing as well.
Today, well-being is defined as a balance between physical and mental aspects. To achieve this, consumers turn to sports, meditation, healthy eating, as well as natural cosmetics products and food supplements that make them feel good. This profound change in lifestyle also echoes with consumers' growing demand for naturality. Faced with this trend, companies need to adapt their offer to meet consumer needs.
6) In today's nutraceutical and nutricosmetics landscape, traditional galenic formats such as capsules and tablets are widely represented and are the reference formats. However, they coexist with innovative alternatives that are closer to food formats. In recent years, we have seen a major shift in consumer habits, with the emergence of new formats such as gummies, shots and drinks. Gummies can be perceived as pleasant snacks evoking childhood memories, while liquid formats offer the possibility of quick and easy consumption, adapted to an often hectic modern lifestyle.
This "foodification" of nutraceuticals goes beyond promoting better consumer compliance. It fits perfectly into an overall wellness ritual for a more holistic approach. Indeed, we're witnessing the emergence of sticks, powders and drinks with flavors that fit perfectly into morning, afternoon or evening wellness routines, such as matcha, coffee (cappuccino), chocolate, etc. to be mixed with water or milk.
Today, there is a wide range of products to suit everyone's needs and tastes. Innovative formats are appearing in all geographic zones, although there are certain specificities depending on the region. For example, some consumers believe that reference formats are more effective than more innovative ones. In 2022, 59% of French VMS users (Vitamins and Minerals Supplements) believed that tablets were more efficient than other formats (1). This is why certain geographical areas are more likely to witness the rapid emergence of new formats. When conducting clinical studies, reference formats such as capsules are mostly found, but formats such as gummies are increasingly present in consumer tests.
12) The solutions offered by nutraceuticals are becoming more comprehensive, catering to the specific needs of multiple target populations.
In this context, Seppic, manufacturer and supplier of nutricosmetic actives, has developed a beauty solution that targets menopausal women. Backed by a total of three clinical studies, Seppic's natural wheat lipidic extract containing phytoceramides appears to be a valuable solution for women seeking to meet the skin and hair challenges associated with menopause.
In 2023, a gold standard randomized double blind placebo controlled clinical trial demonstrated significant results on a subgroup of menopausal women in only two weeks and at a low dose of 30mg/d. Seppic’s active ingredient led to a significant 19% increase in skin moisturization and an 18% improvement in skin elasticity, after 56 days compared to a placebo. Volunteers in the study also reported positive effects on skin roughness and skin smoothness (2).
This ingredient also demonstrated, in 2023, hair benefits on a subgroup of 31 menopausal women during a gold standard randomized double blind placebo controlled clinical trial with the same dosage (post-hoc analysis). The results showed a significant effect on hair growth with +5000 anagen after 84 days vs. DO and an 18% decrease in telogen hair proportion associated with an anti-hair loss effect (3).
What is required to scale-up production of alternative protein sources, such as lab-grown meat and cultivated (breast/bovine) milk?
For the production of 1 kg meat approx. 1 thousand times more water is needed than for 1 kg grain. And furthermore 60% of grain production in Germany is used for feeding cattle and pork.
The development of automated production equipment for tailor-made cultured meat using 3D bioprinting will help to feed the world (4).
The 3D bioprinting technology was developed by Professor Matsusaki of the Osaka University to create muscle tissue structures. This technology is expected to be utilized in the field of food, for production of cultured meat with controlled arrangement of muscle, fat, and blood vessels.
Most of the cultured meats reported so far have a minced structure consisting only of muscle cells, making it difficult to reproduce complex structures. To solve this problem, Matsusaki and co-workers developed a 3D bioprinting technology that uses 3D printing to produce different fibrous tissues (muscle, fat, and blood vessels) and integrates them into a bundle. This technology has made it possible not only to reproduce the famous Wagyu beef, but also to delicately adjust the fat and muscle components. Osaka University and Shimadzu will jointly develop equipment to automate the production of cultured meat using this technology. (5).
What are the most effective methods for enhancing the flavor and texture of alternative proteins?There are meaningful reasons not to go for these new types of foods
Bad experience in terms of taste and texture
Raw meat on its own has little aroma; therefore, almost all aromas associated with “meatiness” are created during the cooking process by the Maillard Reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars. That reaction determines which non-volatile precursors release volatile aroma compounds. Plant-based meat (PBM), products created to resemble animal meat in both look and taste, are growing in popularity. A plant protein such as soy protein concentrate, along with colors, stabilizers, and oils, is used to successfully mimic meat flavor and texture. And, just like in animal meat, the amino acids of that protein undergo the Maillard Reaction.
Samples of PBM were run with the solid phase microextraction GC-MS and the volatile profile was compared against that of the organic beef. Similar compounds, such as fatty acids and Maillard browning reaction products, were found in both types of meat (Figure 1).
The differences can be explained by the different and wide variety of precursors present in PBM since it contains amino acids and sugars from various sources as opposed to regular meat.
There are five basic tastes, including deliciousness, which are perceived by people. The amount and kind of amino acids contribute to taste components. Of all the amino acids, glutamic acid is widely known as a component of the delicious taste. Further, the types and component ratios of amino acids largely control the flavor of food products. For example, glycine and alanine are associated with sweetness, valine and leucine with bitterness, and aspartic acid and glutamic acid with deliciousness.
The texture of food, including the sense of crispness, springiness, firmness, and the feeling on the tongue, is an important element that together with taste has an impact on the deliciousness of food. Food texture is normally evaluated using sensory tests. However, sensory tests are often difficult to reproduce, due to individual differences in people’s sensations and physical condition.
A texture analyzer can support sensory test with objective results in the form of numerical values for use in the field of food development. The texture analyzer evaluates the texture characteristics and allows a comparison of the texture of plant-based meat (PBM) and, for instance, chicken meatballs. Compared to chicken-derived products, plant-based meatballs had a higher force under loading conditions with less elasticity, which is the property to restore deformation (6). It is consistent with the result of the sensory test.
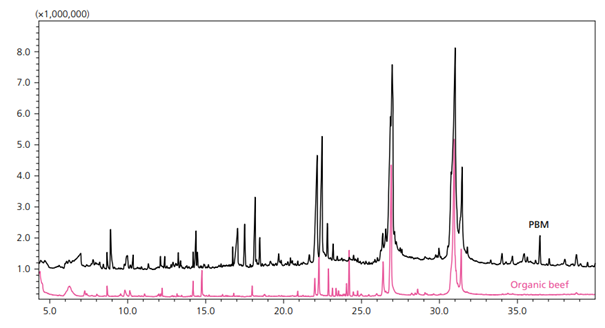
Figure 1. Overlaid Representative Chromatograms for PBM (black) and Organic Beef (pink) (6).
Panelists
References and notes
- A report from Mintel Consulting for Seppic (February 2022)
- Kern, C., Dudonné, S., & Garcia, C. (2023). Dietary supplementation with a wheat polar lipid complex improves skin conditions in women with dry skin and mild‐to‐moderate skin aging. Journal Of Cosmetic Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.16130
- Dudonné, S., Kern, C., & Garcia, C. (2023). Efficacy of a wheat polar‐lipid complex in reducing hair loss and improving hair growth in healthy women : a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical study. International Journal of Cosmetic Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/ics.12929
Questions
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
How have consumer awareness & demands related to healthy lifestyle changed in the last 12 months?
Where do you see the greatest scientific achievement in nutritional sciences in the last 12 months?
Are there specific health benefit areas in which significant more clinical studies are being done than in others, comparing the last 3 years?
What are the key influencers driving consumer purchasing decision for supplements or health foods? Is substantiation of claims important?
How do consumer today judge their health status?
Please put the following parameter in order 1 highest priority 7 lowest priority:
- Physical Symptoms, like pain, fatigue, constipation, weight gain
- Fitness Levels: endurance, strength, flexibility,
- Health Tracking Devices and heart rate, sleep patterns, steps taken
- Diet and Nutrition: intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins.
- Mental and Emotional Well-being: stress levels, emotional balance, happiness
- Quality of sleep: Sleep quality and duration
- Medical Check-ups: blood pressure checks, cholesterol screenings, blood sugar tests
6.
Delivery formats can support consumer compliance and underline the technology driven approach of the brand.
a.
b.
c.
Do you see a consumer trend in preferences for certain delivery formats?
Are delivery format preference a regional, cultural aspect like taste?
Do you see a trend to carry out ingredient clinical trials using a selected delivery format as study product formulation or are most clinical studies still done in capsules?
7.
Consumer health concerns can vary widely across different regions and demographics globally. However, several common health concerns tend to be prevalent across various countries and populations due to globalization, lifestyle changes, environmental factors, and access to information.
a.
b.
Which are the key global consumer health concerns?
Do you see regional differences?
8.
There is a significant increase in the availability of apps and digital platforms focused on healthy lifestyle, particularly to support personalized approaches to mental wellbeing, metabolic support, weight management and physical fitness.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Do you see lifestyle apps as competition for supplement brands?
Do you think that these apps help to educate consumers, being more targeted when searching for supplements?
Did you consider setting up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement or your ingredient?
Did you set up a lifestyle app to promote your supplement/ ingredient and can you explore about your experience and business impact?
9.
AI (Artificial Intelligence) algorithms are today offered for various aspects of clinical trials to proof efficacy of your health ingredient or supplement.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Are consumers looking for substantiation of claims through AI driven clinical trials?
Did you consider working with an CRO specialist in AI to investigate your health ingredient or supplement?
If you applied already AI methods during the discovers/ development of your health ingredient, please share your experience and recommendation with us.
Do you think that in 2030 AI will be a manifest tool for clinical trials?
10.
A healthy lifestyle may also involve a commitment to sustainable practices for both personal and planetary health. This could include supporting ethical and environmentally conscious products.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Do you agree that sustainability has become a growing concern also in the nutraceutical industry?
Are consumer looking proactively for brands which have ethical and environmental principles?
Are you looking for ethically sourced raw materials, ingredients?
Did you implement measures to establish resource-efficient processes?
Are you developing socially useful products and how do you define it?
11.
What are the major geographical differences related to healthy lifestyle trends?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
What are the latest trends related to claims and product forms in China?
In the U.S.
In Mexico
How are claims and dosage forms differentiated in Europe? How does your company ensure compliance with health and safety regulations in Europe?
Do you have a country where you would like to speak about trends for products?
12.
Focus clinical studies. Overall, there has been a recognized push for more gender-inclusive, geographical, and target group focused clinical research. The same trend can be seen in clinical trials for supplements or functional foods.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Please select an area you are active in and let us know which is your hot topic ingredients for 2024 for this area, based on substantiated claim, parameters, biomarkers being studied and/ or clinical study being done. Please name ingredients by scientific name and composition and not by brand name.
Please select your geographical area:
Western (EU, USA)
Asia (China, Japan, Asia Pacific)
Americas (Middle and Latin America)
Kids development/ early life nutrition/infant in Western countries and AP
Adult nutrition and prevention of developing disease
Elderly nutrition and how to support quality of life during aging
Sports nutrition, within different life decades and activity levels
References and notes























